How do I choose my respiratory protection ?
 When choosing your respiratory protection equipment, it is important to identify the nature of the hazards related to your function!
When choosing your respiratory protection equipment, it is important to identify the nature of the hazards related to your function! Do you breathe on a daily basis :
 Fumes?
Fumes?Fumes are formed when a solid material evaporates under the effect of high heat and then condenses. For example, metal vapours cool down and condense into very fine particles, usually less than 1 micron in diameter. Metal fumes can result from operations such as welding, melting or spilling molten metals.
Gases?
That is, substances that are similar to air in their ability to spread freely in a container or area. Examples include oxygen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen or helium.
Dust?
Dust is formed when solid materials are disintegrated into fine particles floating in the air before settling under the effect of gravity. Dust is produced by operations such as grinding, drilling, sanding, blasting and milling.
Vapors?
That is, the gaseous state of substances being either in a liquid or solid state at room temperature.
 Dust masks and filters
Dust masks and filters
Dust filters are classified in 3 classes :
- P1: Inert dusts (5 x limit value)
- P2 :Harmful agents (10 x limit value)
- P3: Toxic agents (50 x limit value with half mask / 100 x limit value with full mask )
 Gas masks and filters
Gas masks and filters
Gas filters generally contain activated carbon to retain gas molecules. Activated carbon is often impregnated with other materials, to which the gases are chemically bound. It is essential to adapt the choice of your filter to the gas or groups of gases you are dealing with.
They are classified with a letter and a color, according to the type of products or substances they retain:
- A (Brown): Organic vapors
- B (Grey): Acidic gases and vapours such as halogens, hydrohalic acids, hydrocyanic acids, hydrosulfuric acids, phosgene...
- E (Yellow): Sulphur dioxide, hydrochloric acid
- K (Green): Ammonia, amine, hydrazine
- CO (Grey with black stripes): Carbon monoxide
- AX: Organic products at low boiling temperature (<65C°)
- SX (Violet): Specific compounds (Hg, NO...)(<65C°)
- 1 max. 1000 ppm
- 2 max. 5000 ppm
- 3 max. 10000 ppm
- Type of gas filters: A, B, E, K
- Gas filter class: 1, 2, 3
- Dust filter class: P1, P2, P3
Do you need advice on choosing your product? Call our specialists at +32 (0)4 224 99 99, from Monday to Friday from 8:30 am to 5:00 pm.
Best-selling respiratory protection products
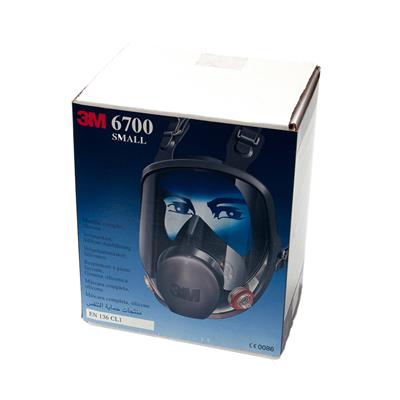
3M 6700S Silicone rubber full face mask - Low maintenance - Size small - per piece
Item No. 11115920
€ 168,82
Add to cart
€ 168,82
Add to cart
3M 6055 A2 Organic Gas and Vapour Filter - Box of 4 pairs
Item No. 11115924
€ 73,28
Add to cart
3M 6099 Combined filter A2B2E2K2HgP3 + Formaldehyde - Box of 2 pairs
Item No. 11115929
€ 26,48
Add to cart
€ 188,00
Add to cart
€ 45,42
Add to cart




 Dust
Dust Gas
Gas